Asme Y14 5m 2009
ASME Y14.5-2009 geometric dimensioning and tolerancing ( GD&T ) is a language of symbols used on mechanical drawings to efficiently, and accurately communicate geometry requirements for features on parts and assemblies. GD&T is, and has been, successfully used for many years in the automotive, aerospace, electronic and the commercial design and manufacturing industries.
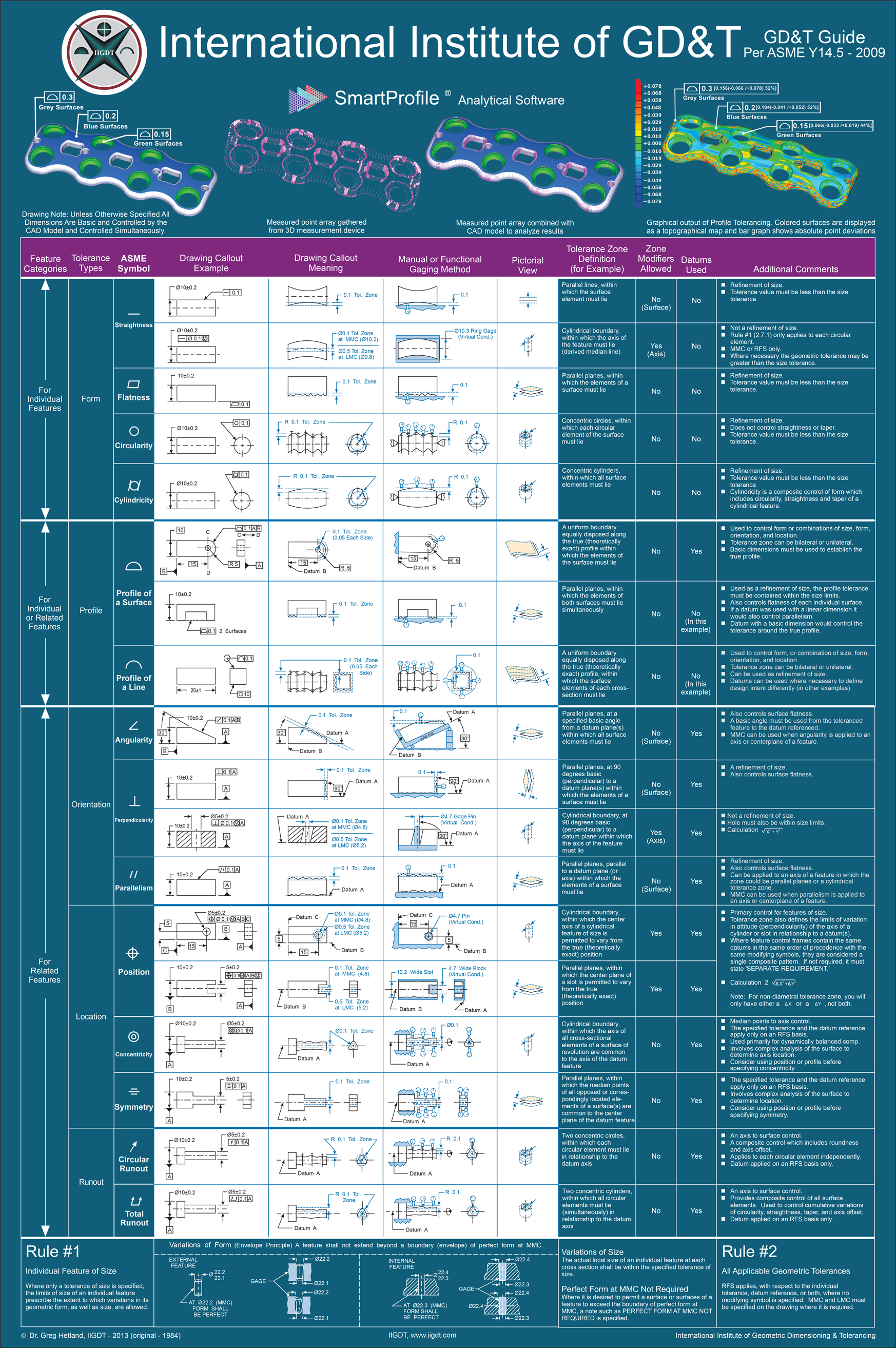
GD&T, both ASME Y14.5-2009 and Geometrical Product Specifications ISO series are the only recognized international drawing standards in use throughout the world. The ASME Y14.5-2009 and Geometrical Product Specifications ISO 1101(e)-2004 series are very similar and provide identical means to specifiy dimensional requirements. What are the Advantages? In today's modern and technically advanced design, engineering and manufacturing world, effective communication is required to ensure the design and manufacture of successful products.
One such standard is American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) Y14.5-2009. This article is based on that standard. Changes and Additions to The Eagle Shooting Heroes 2008 Sub Indo. ASME Y14.5M. ASME Y14.5 2009 Standard! 2009-07-31 Bill Tandler With editorial contributions from Evan Janeshewski and Ron Grube Multi Metrics & SmartGD&T 1.
Success oriented organizations, which require accurate and common lines of communications between engineering, design, manufacturing, and quality should consider (GD& T) as their mechanical drawing standard. Some distinct advantages of GD&T are as follows: GD&T facilitates an efficient means to communicate specific datums on a part. A datum is just a fancy word for saying which specific feature on a part will be used as a reference (zero) for tolerance calculations, dimensional measurement, and most importantly, from where the feature(s) manufacturing should build from to ensure a consistent part. Without the use of a datum system (zero reference) on a part, it is not clear to manufacturing or quality where to manufacture or measure from. Additionally, the use of datums dramatically simplifies the design and specification of fixtures for use in manufacturing and quality verification steps.
GD&T allows the use of round tolerance zones as opposed to square or rectangular tolerance zones as given by limit tolerancing methods for cylindrical (holes, shafts) features. In the mechanical drawing given in figure 1, there are four holes drilled thru the block, and each hole's location relative to each other and the edges are specified using a limit tolerance of a distance and +.005 and.005. This means the derived center of each of the holes must fall within a square tolerance zone.010 x.010 at some location, which as illustrated in figure 2. Figure 1 Figure 2 In figure 2, there is a dimension attached to the top left and bottom right corners.
This is the actual worst scenario for which the hole features may be manufactured (.014 or +.007 and.007). Therefore, a square tolerance zone defined at +.005 and.005 is actually +.007 and.007 worst case. Assuming the that this part must be interchangeable, or always fits in the target assembly when manufactured as specified above, then the +.007 and.007 is the real worst case scenario (not +.005.005). In geometric dimensioning and tolerancing, cylindrical features may be located with round or cylindrical tolerance zones.
Round tolerance zones offer several distinct advantages over square or rectangular tolerance zones. In figure 3, we have overlaid a round tolerance zone over our square tolerance zone for the part given in Figure 1. Chota Bheem Vs Aliens Cricket Match Full Movie. The shaded areas represent the increase in tolerance available by using round tolerance zone equivalent to the specified square tolerance zone in figure 1. As you can see, the hole may now be manufactured within the shaded areas where the square tolerance zone ends to the right, left, top, bottom at.007 off perfect center. The Reef 2006 Rapidshare. This increase in available tolerance is equal to approximately 57%. A round tolerance zone is simply less expensive to manufacture, additionally GD&T allows for material modifiers, which allow for up to several hundred percent increase in tolerance, reducing manufacturing difficulty even more while maintaining interchangeability requirements. Additionally, because the tolerance zones are round this allows the specification of similar features (round pin for a hole) on 'quick check' tools, such as go and no-go fixtures, where with square or rectangular tolerance zones, the verification tool requirements are not clear.



